#include <rpm_calculator.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| RpmCalculator () | |
| operation_mode_e | getOperationMode () const override |
| void | onSlowCallback () |
| bool | isStopped () const override |
| bool | isSpinningUp () const |
| bool | isCranking () const override |
| bool | isRunning () const |
| bool | checkIfSpinning (efitick_t nowNt) const |
| spinning_state_e | getState () const |
| void | setSpinningUp (efitick_t nowNt) |
| void | setStopSpinning () |
| float | getCachedRpm () const |
| void | onNewEngineCycle () |
| uint32_t | getRevolutionCounterM (void) const |
| void | setRpmValue (float value) |
| void | assignRpmValue (float value) |
| uint32_t | getRevolutionCounterSinceStart (void) const |
| float | getRpmAcceleration () const |
| float | getSecondsSinceEngineStart (efitick_t nowNt) const |
| floatus_t | getOneDegreeUs () override |
 Public Member Functions inherited from StoredValueSensor Public Member Functions inherited from StoredValueSensor | |
| SensorResult | get () const final override |
| StoredValueSensor (SensorType type, efidur_t timeoutNt) | |
| void | invalidate () |
| void | invalidate (UnexpectedCode why) |
| void | setValidValue (float value, efitick_t timestamp) |
| void | showInfo (const char *sensorName) const override |
| virtual void | setTimeout (int timeoutMs) |
 Public Member Functions inherited from Sensor Public Member Functions inherited from Sensor | |
| bool | Register () |
| const char * | getSensorName () const |
| virtual bool | hasSensor () const |
| virtual float | getRaw () const |
| virtual bool | isRedundant () const |
| void | unregister () |
| SensorType | type () const |
Data Fields | |
| float | previousRpmValue = 0 |
| floatus_t | oneDegreeUs = NAN |
| Timer | lastTdcTimer |
| float | rpmRate = 0 |
Protected Member Functions | |
| void | showInfo (const char *sensorName) const override |
 Protected Member Functions inherited from Sensor Protected Member Functions inherited from Sensor | |
| Sensor (SensorType type) | |
Private Attributes | |
| float | cachedRpmValue = 0 |
| uint32_t | revolutionCounterSinceBoot = 0 |
| uint32_t | revolutionCounterSinceStart = 0 |
| spinning_state_e | state = STOPPED |
| bool | isSpinning = false |
| Timer | engineStartTimer |
Additional Inherited Members | |
 Static Public Member Functions inherited from Sensor Static Public Member Functions inherited from Sensor | |
| static void | showAllSensorInfo () |
| static void | showInfo (SensorType type) |
| static void | resetRegistry () |
| static const Sensor * | getSensorOfType (SensorType type) |
| static SensorResult | get (SensorType type) |
| static float | getOrZero (SensorType type) |
| static float | getRaw (SensorType type) |
| static bool | isRedundant (SensorType type) |
| static bool | hasSensor (SensorType type) |
| static void | setMockValue (SensorType type, float value, bool mockRedundant=false) |
| static void | setInvalidMockValue (SensorType type) |
| static void | resetMockValue (SensorType type) |
| static void | resetAllMocks () |
| static void | inhibitTimeouts (bool inhibit) |
| static const char * | getSensorName (SensorType type) |
 Static Protected Attributes inherited from Sensor Static Protected Attributes inherited from Sensor | |
| static bool | s_inhibitSensorTimeouts = false |
Detailed Description
Most consumers should access value via Sensor framework by SensorType::Rpm key
Definition at line 42 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ RpmCalculator()
| RpmCalculator::RpmCalculator | ( | ) |
Definition at line 98 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Member Function Documentation
◆ assignRpmValue()
| void RpmCalculator::assignRpmValue | ( | float | value | ) |
The same as setRpmValue() but without state change. We need this to be public because of calling rpmState->assignRpmValue() from rpmShaftPositionCallback()
this would make sure that we have good numbers for first cranking revolution #275 cranking could be improved
Definition at line 134 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
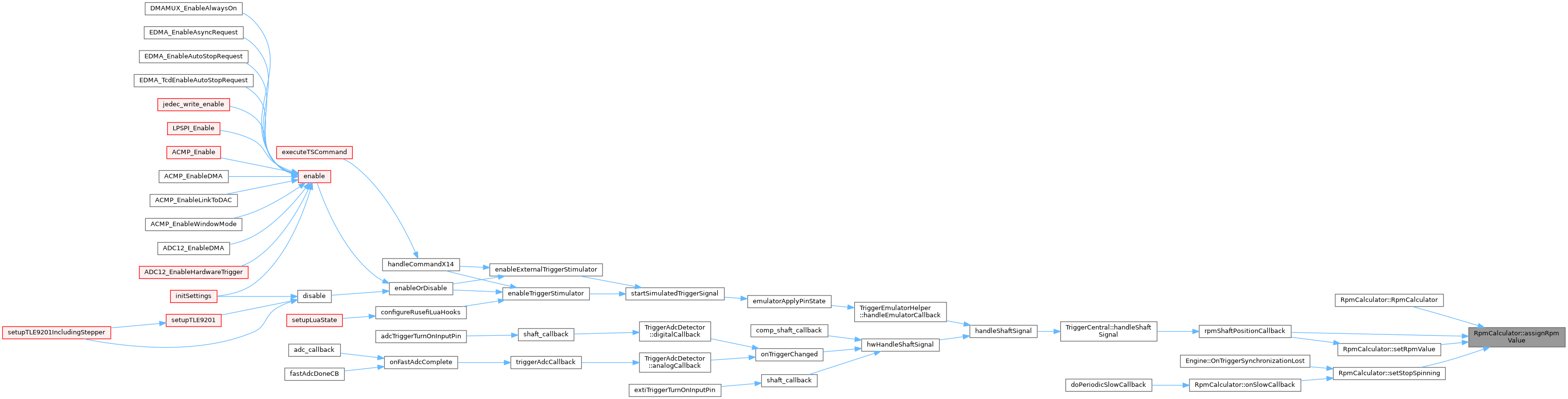
Referenced by RpmCalculator(), rpmShaftPositionCallback(), setRpmValue(), and setStopSpinning().
◆ checkIfSpinning()
| bool RpmCalculator::checkIfSpinning | ( | efitick_t | nowNt | ) | const |
- Returns
- true if engine is spinning (cranking or running)
Also check if there were no trigger events
Definition at line 114 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by rpmShaftPositionCallback().


◆ getCachedRpm()
| float RpmCalculator::getCachedRpm | ( | ) | const |
Just a quick getter for rpmValue Should be same exact value as Sensor::get(SensorType::Rpm).Value just quicker. Open question if we have any cases where this opimization is needed.
Definition at line 49 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by TriggerCentral::handleShaftSignal(), and mainTriggerCallback().

◆ getOneDegreeUs()
|
inlineoverridevirtual |
Implements EngineRotationState.
Definition at line 121 of file rpm_calculator.h.
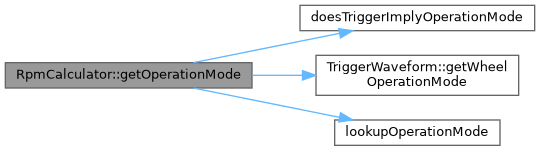
◆ getOperationMode()
|
overridevirtual |
Implements EngineRotationState.
Definition at line 81 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
◆ getRevolutionCounterM()
| uint32_t RpmCalculator::getRevolutionCounterM | ( | void | ) | const |
Definition at line 204 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
◆ getRevolutionCounterSinceStart()
| uint32_t RpmCalculator::getRevolutionCounterSinceStart | ( | void | ) | const |
Definition at line 45 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
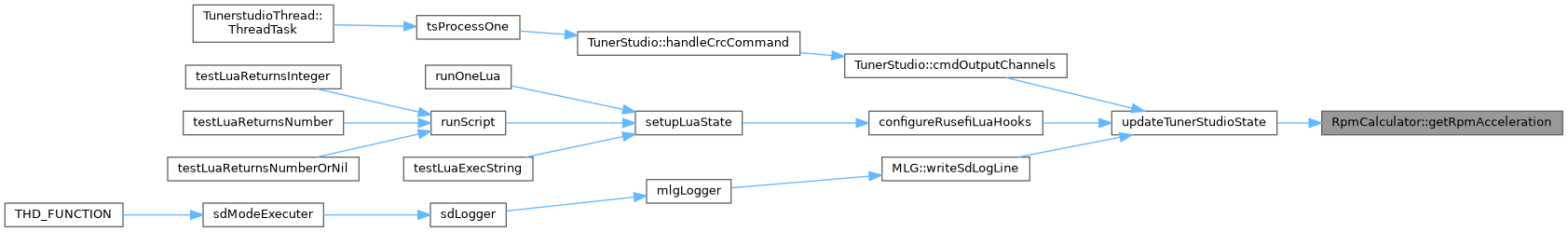
Referenced by getCrankingFuel(), IdleController::getCrankingTaperFraction(), getPostCrankingFuelCorrection(), and updateTunerStudioState().

◆ getRpmAcceleration()
| float RpmCalculator::getRpmAcceleration | ( | ) | const |
RPM rate of change between current RPM and RPM measured during previous engine cycle see also SC_RPM_ACCEL
Definition at line 27 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by updateTunerStudioState().
◆ getSecondsSinceEngineStart()
| float RpmCalculator::getSecondsSinceEngineStart | ( | efitick_t | nowNt | ) | const |
Definition at line 323 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
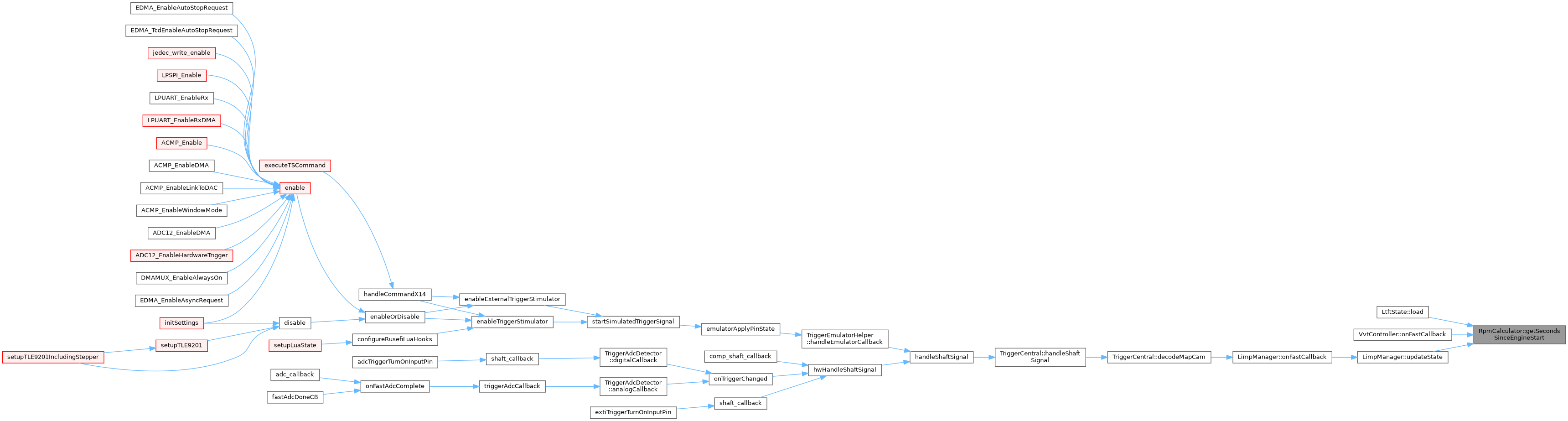
Referenced by LtftState::load(), VvtController::onFastCallback(), and LimpManager::updateState().
◆ getState()
| spinning_state_e RpmCalculator::getState | ( | ) | const |
This accessor is used in unit-tests.
Definition at line 195 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by configureRusefiLuaHooks().

◆ isCranking()
|
overridevirtual |
Returns true if the engine is cranking OR spinning up
Implements EngineRotationState.
Definition at line 36 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
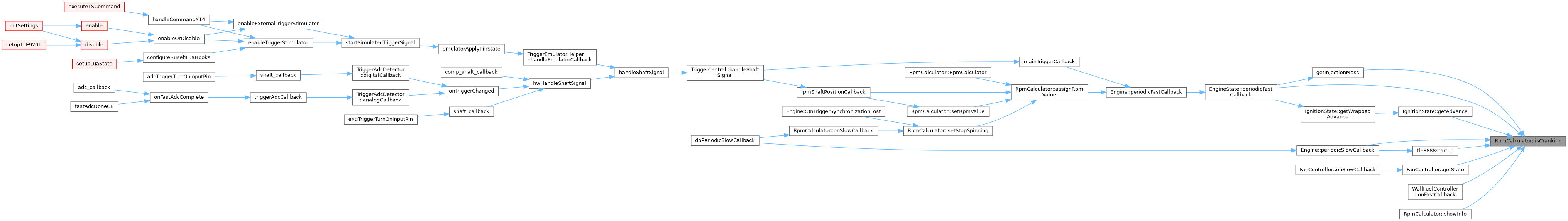
Referenced by IgnitionState::getAdvance(), getInjectionMass(), FanController::getState(), WallFuelController::onFastCallback(), EngineState::periodicFastCallback(), Engine::periodicSlowCallback(), showInfo(), and tle8888startup().
◆ isRunning()
| bool RpmCalculator::isRunning | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if the engine is running and not cranking
- Returns
- true if there was a full shaft revolution within the last second
Definition at line 107 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by IdleController::determinePhase(), disengageStarterIfNeeded(), ShortTermFuelTrim::getCorrectionState(), FanController::getState(), TripOdometer::onSlowCallback(), Engine::periodicSlowCallback(), StepperMotorBase::setInitialPosition(), showInfo(), startKnockSampling(), startStopButtonToggle(), and LimpManager::updateState().
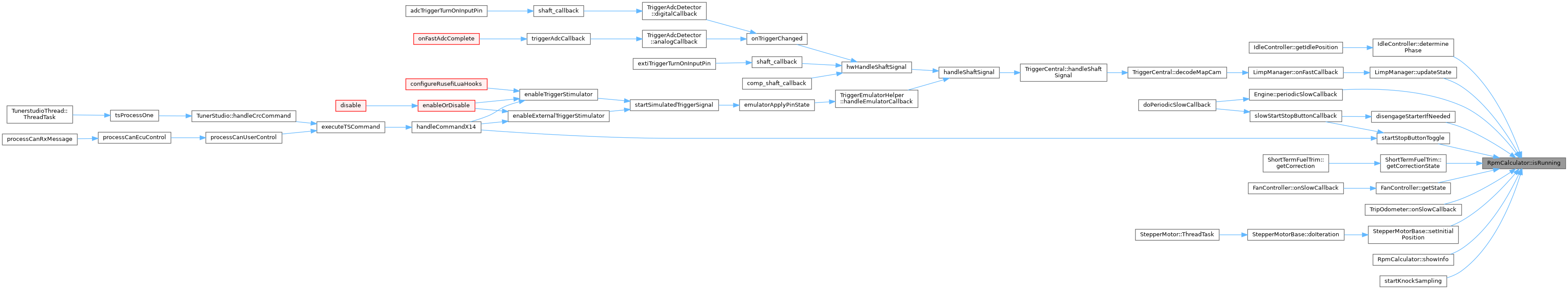
◆ isSpinningUp()
| bool RpmCalculator::isSpinningUp | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if the engine is spinning up
Definition at line 41 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by getCurrentIgnitionMode(), rpmShaftPositionCallback(), setSpinningUp(), and showInfo().
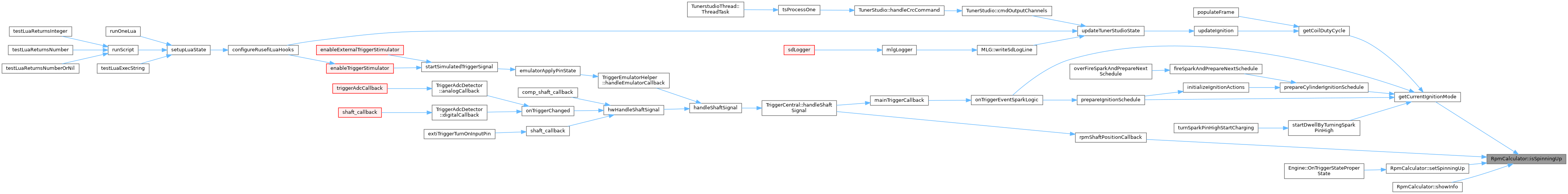
◆ isStopped()
|
overridevirtual |
Returns true if the engine is not spinning (RPM==0)
Implements EngineRotationState.
Definition at line 31 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
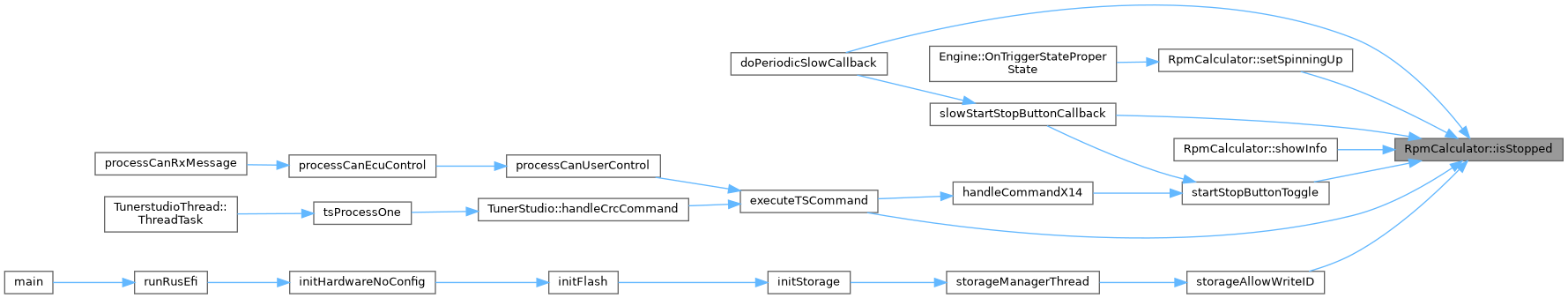
Referenced by doPeriodicSlowCallback(), executeTSCommand(), setSpinningUp(), showInfo(), slowStartStopButtonCallback(), startStopButtonToggle(), and storageAllowWriteID().
◆ onNewEngineCycle()
| void RpmCalculator::onNewEngineCycle | ( | ) |
This method is invoked once per engine cycle right after we calculate new RPM value
Definition at line 199 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by rpmShaftPositionCallback().

◆ onSlowCallback()
| void RpmCalculator::onSlowCallback | ( | ) |
Definition at line 208 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by doPeriodicSlowCallback().
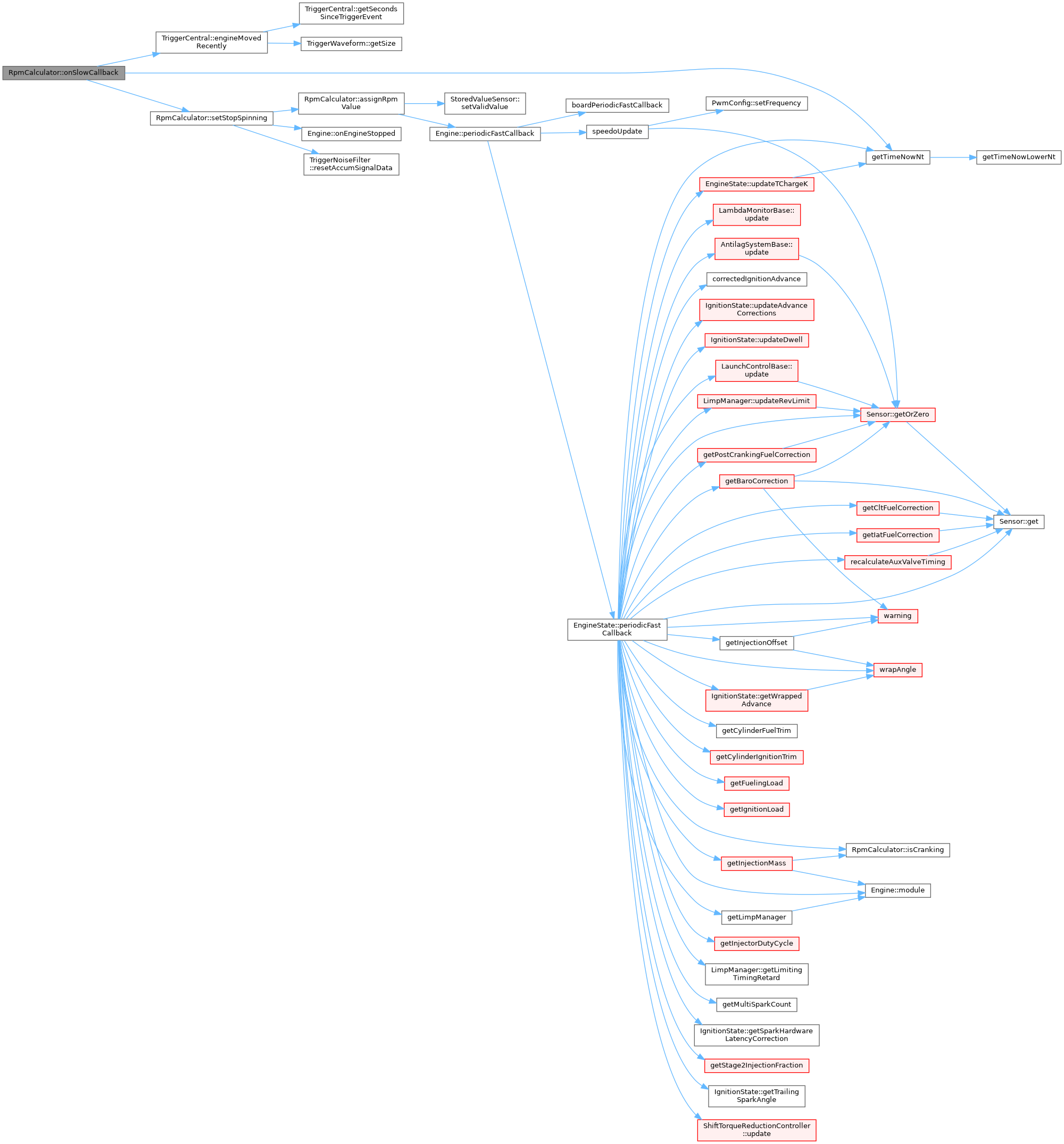

◆ setRpmValue()
| void RpmCalculator::setRpmValue | ( | float | value | ) |
We are here if RPM is above zero but we have not seen running RPM yet. This gives us cranking hysteresis - a drop of RPM during running is still running, not cranking.
Definition at line 155 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by rpmShaftPositionCallback().
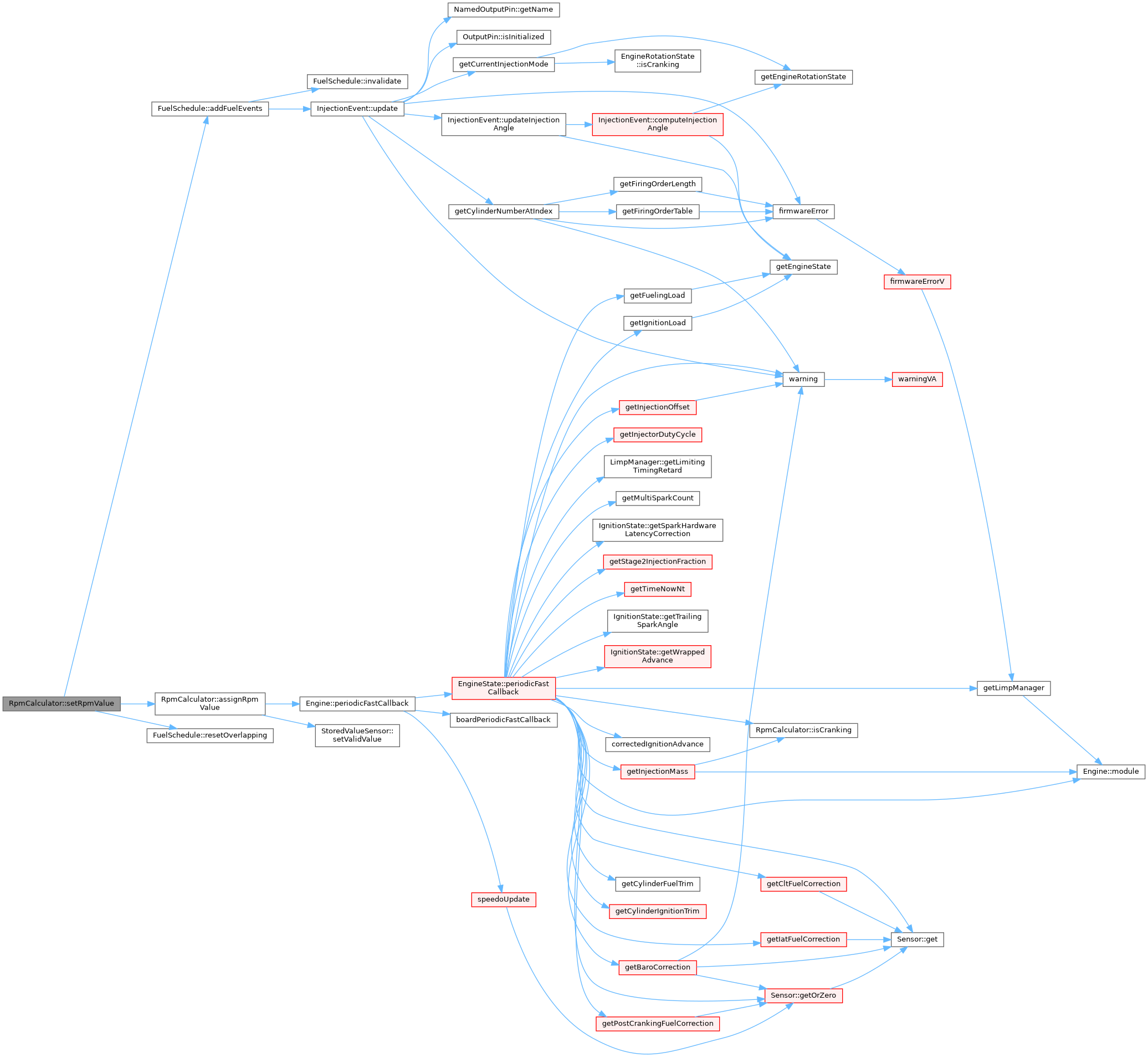
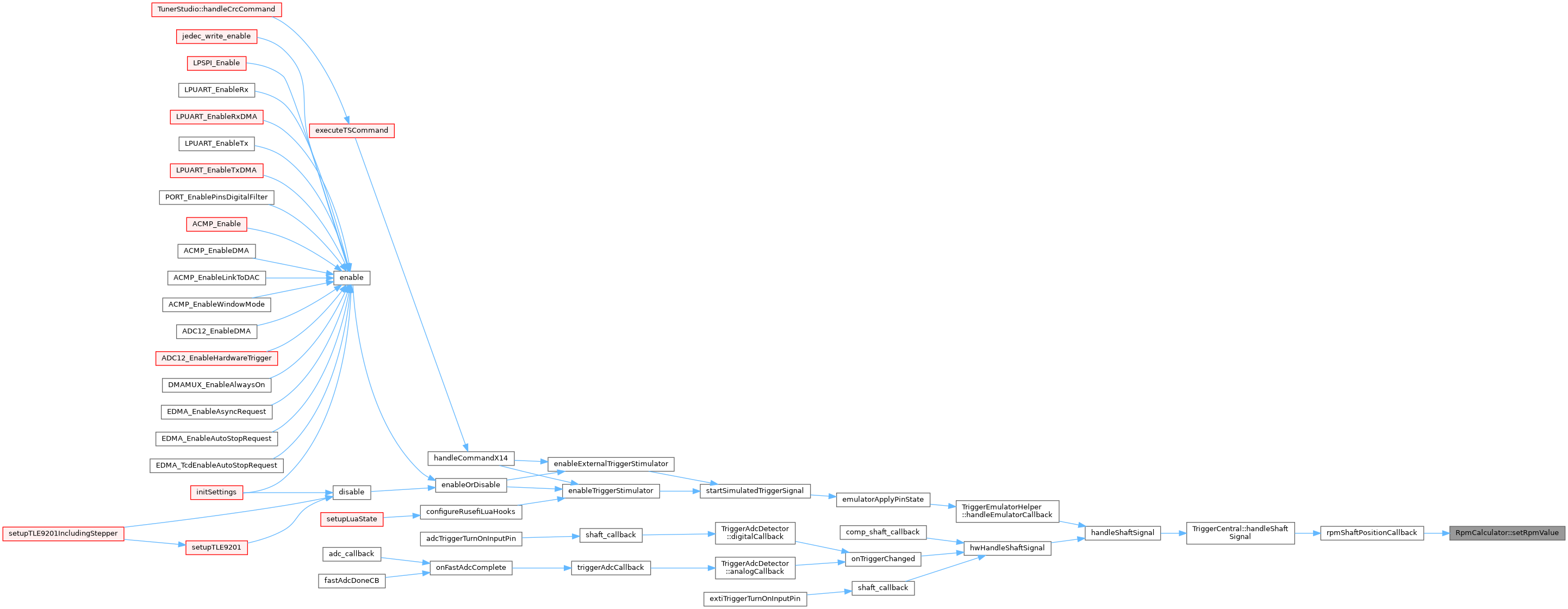
◆ setSpinningUp()
| void RpmCalculator::setSpinningUp | ( | efitick_t | nowNt | ) |
Should be called on every trigger event when the engine is just starting to spin up.
Definition at line 231 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by Engine::OnTriggerStateProperState().
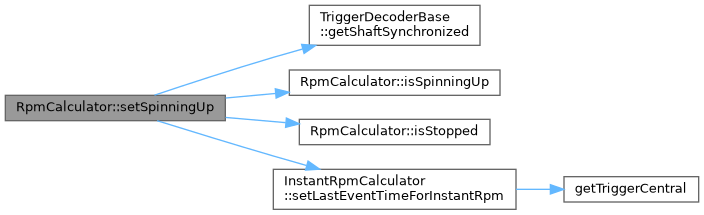
◆ setStopSpinning()
| void RpmCalculator::setStopSpinning | ( | ) |
Called if the synchronization is lost due to a trigger timeout.
Definition at line 215 of file rpm_calculator.cpp.
Referenced by onSlowCallback(), and Engine::OnTriggerSynchronizationLost().

◆ showInfo()
|
overrideprotectedvirtual |
Implements Sensor.
Definition at line 66 of file sensor_info_printing.cpp.

Field Documentation
◆ cachedRpmValue
|
private |
At this point this value is same exact value as in private m_value variable At this point all this is performance optimization? Open question is when do we need it for performance reasons.
Definition at line 140 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Referenced by assignRpmValue(), getCachedRpm(), isCranking(), isStopped(), setRpmValue(), and setStopSpinning().
◆ engineStartTimer
|
private |
Definition at line 160 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Referenced by getSecondsSinceEngineStart(), and setRpmValue().
◆ isSpinning
|
private |
True if the engine is spinning (regardless of its state), i.e. if shaft position changes. Needed by spinning-up logic.
Definition at line 158 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Referenced by setSpinningUp(), and setStopSpinning().
◆ lastTdcTimer
| Timer RpmCalculator::lastTdcTimer |
Definition at line 125 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Referenced by checkIfSpinning(), PrimaryTriggerDecoder::onTriggerError(), and rpmShaftPositionCallback().
◆ oneDegreeUs
| floatus_t RpmCalculator::oneDegreeUs = NAN |
This is a performance optimization: let's pre-calculate this each time RPM changes NaN while engine is not spinning
Definition at line 119 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Referenced by assignRpmValue(), TriggerCentral::getCurrentEnginePhase(), getOneDegreeUs(), IgnitionState::getSparkHardwareLatencyCorrection(), scheduleByAngle(), and startKnockSampling().
◆ previousRpmValue
| float RpmCalculator::previousRpmValue = 0 |
this is RPM on previous engine cycle.
Definition at line 113 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Referenced by assignRpmValue(), and rpmShaftPositionCallback().
◆ revolutionCounterSinceBoot
|
private |
This counter is incremented with each revolution of one of the shafts. Could be crankshaft could be camshaft.
Definition at line 146 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Referenced by getRevolutionCounterM(), and onNewEngineCycle().
◆ revolutionCounterSinceStart
|
private |
Same as the above, but since the engine started spinning
Definition at line 150 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Referenced by getRevolutionCounterSinceStart(), onNewEngineCycle(), and setStopSpinning().
◆ rpmRate
| float RpmCalculator::rpmRate = 0 |
Definition at line 128 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Referenced by getRpmAcceleration(), rpmShaftPositionCallback(), and setStopSpinning().
◆ state
|
private |
Definition at line 152 of file rpm_calculator.h.
Referenced by getState(), isCranking(), isRunning(), isSpinningUp(), isStopped(), setRpmValue(), setSpinningUp(), and setStopSpinning().
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- controllers/engine_cycle/rpm_calculator.h
- controllers/engine_cycle/rpm_calculator.cpp
- controllers/sensors/sensor_info_printing.cpp