Detailed Description
A single upcounting timer (currently TIM5) is used as a single timebase both for time measurement and event scheduling. This helps reduce jitter by not making another time measurement at the time of scheduling.
This implementation only works on stm32 because it sets hardware registers directly. ChibiOS doesn't support using timers in output compare mode, only PMW, so we have to manually configure the timer in outupt compare mode.
- Date
- Dec 1, 2020
Definition in file microsecond_timer_stm32.cpp.
Functions | |
| void | portSetHardwareSchedulerTimer (efitick_t nowNt, efitick_t setTimeNt) |
| static void | hwTimerCallback (PWMDriver *) |
| void | portInitMicrosecondTimer () |
| uint32_t | getTimeNowLowerNt () |
Variables | |
| static constexpr PWMConfig | timerConfig |
Function Documentation
◆ getTimeNowLowerNt()
| uint32_t getTimeNowLowerNt | ( | ) |
Get a monotonically increasing (but wrapping) 32-bit timer value Implemented at port level, based on timer or CPU tick counter Main source of EFI clock, SW-extended to 64bits
2147483648 / ~168MHz = ~12 seconds to overflow
Definition at line 73 of file microsecond_timer_stm32.cpp.
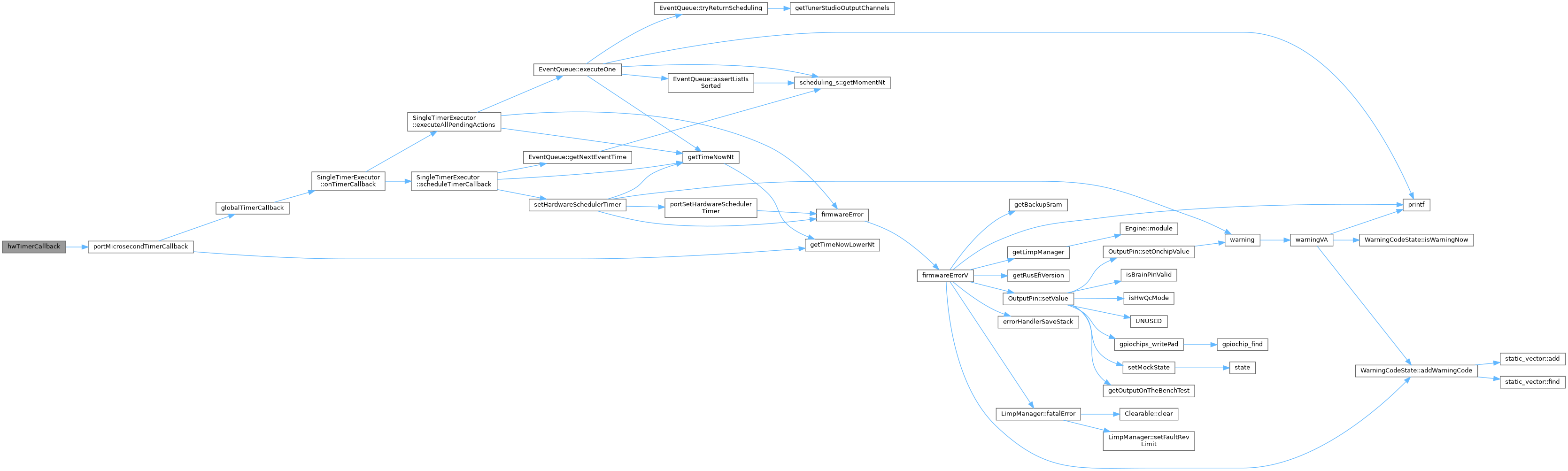
◆ hwTimerCallback()
|
static |
Definition at line 30 of file microsecond_timer_stm32.cpp.
◆ portInitMicrosecondTimer()
| void portInitMicrosecondTimer | ( | ) |
This file defines the API for the microsecond timer that a port needs to implement
Do not call these functions directly, they should only be called by microsecond_timer.cpp
Definition at line 54 of file microsecond_timer_stm32.cpp.
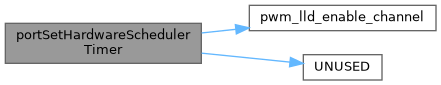
◆ portSetHardwareSchedulerTimer()
| void portSetHardwareSchedulerTimer | ( | efitick_t | nowNt, |
| efitick_t | setTimeNt | ||
| ) |
Definition at line 22 of file microsecond_timer_stm32.cpp.
Variable Documentation
◆ timerConfig
|
staticconstexpr |
Definition at line 35 of file microsecond_timer_stm32.cpp.
Referenced by portInitMicrosecondTimer().